Acas Capability Dismissal
Step 1: Understanding the options
The EAT has confirmed that the Acas Code of Practice does not apply to dismissals for ill health capability. In Holmes v Qinetiq t he Claimant was dismissed on the grounds of ill health and his employees conceded that the dismissal was unfair because of the failure to obtain an up to date occupational health report. However, the Claimant also argued that the ACAS Code of Practice applied. The outcome may be dismissal which the employee can appeal and potentially bring a tribunal claim in which case all records will be required. The capability process must be fair and transparent and, where the employer does not have a written policy and procedure, it is advisable to follow the Acas Code of Practice for Discipline and Grievance. The EAT held that the ACAS Code of Practice does not apply to ill health dismissals as the ACAS Code of Practice, properly construed, does not apply to an employer’s internal procedures concerning alleged incapability to undertake a role because of sickness absence; the EAT held that the ACAS Code of Practice only applies to procedures concerning allegations of misconduct and poor performance (rather than ill health). Dismissal is a last resort and you should consider as many ways as possible to help the employee back to work, including: getting a medical report from their GP with the employee’s permission. As a matter of best practice, in cases of conduct or capability matters, you should always refer to the guidance set out under the ACAS Code of Practice on Disciplinary and Grievance Procedures. This involves a variety of steps that must be taken before making any decision to dismiss, including written warnings and suitable training, where.
A disciplinary procedure is a formal way for an employer to deal with an employee's:
- unacceptable or improper behaviour ('misconduct')
- performance ('capability')
Before starting a disciplinary procedure, the employer should first see whether the problem can be resolved in an informal way. This can often be the quickest and easiest solution.
The employer could try solving the issue with their employee by:
- privately talking with them and any other staff involved
- listening to their point of view
- agreeing improvements to be made
- setting up a training or development plan, if it's a performance issue
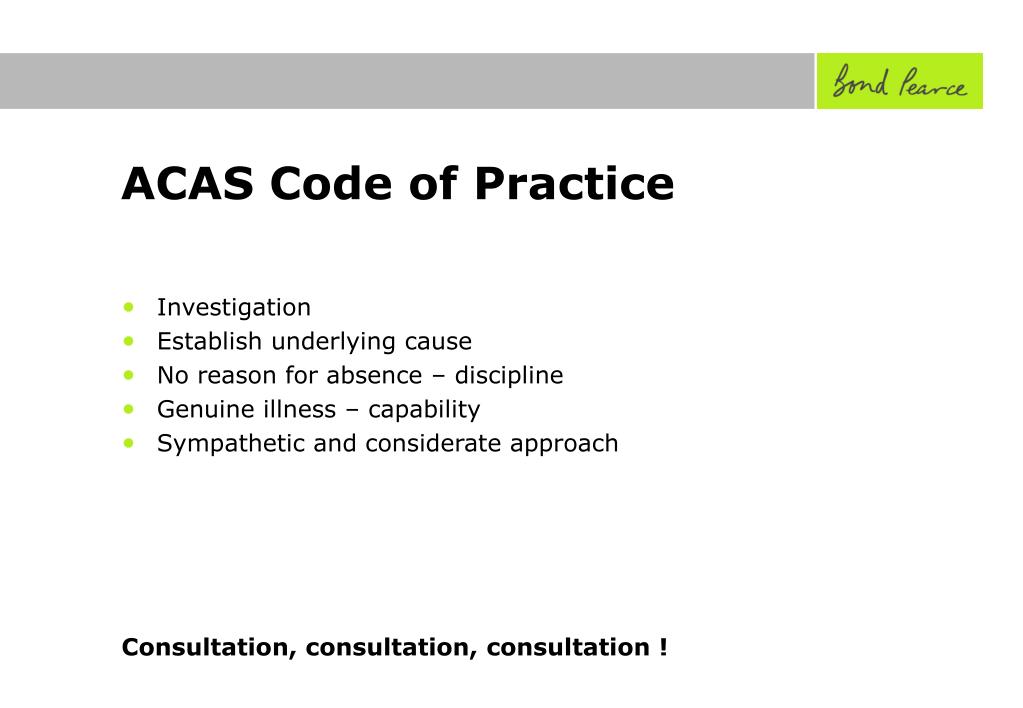
Dealing with capability issues
Capability or performance is about an employee's ability to do the job.
Some employers might have a separate procedure for dealing with capability or performance issues that should be based on:
- support
- training
- encouragement to improve
Whether the employer deals with the issue under a capability or disciplinary procedure, they must do so fairly.
What counts as misconduct
Misconduct is when an employee's inappropriate behaviour or action breaks workplace rules.
Some misconduct examples include:

- bullying
- harassment
- refusing to do work ('insubordination')
- being absent without permission (some people call it absent without leave or 'AWOL')

But your workplace might have its own examples.
If misconduct happens outside the workplace
Acas Capability Dismissal Meaning

Acas Capability Dismissal Rules
An employee could face disciplinary action for misconduct outside work.
For example, where an employee's behaviour in front of external clients at the work Christmas party reflects badly on the company.
It depends on how serious the employer sees the misconduct and whether it could have a bad effect on the business.
It's important the employer carries out a thorough investigation and can show the effect on the business.
When there is gross misconduct
Some acts count as 'gross misconduct' because they are very serious or have very serious effects.
If an employer finds there has been gross misconduct, they should still carry out an investigation and the full disciplinary procedure. They might then decide on dismissal without notice or payment in lieu of notice.
Acas Capability Dismissal Vs
Examples of gross misconduct in the workplace could include:
- fraud
- physical violence
- serious lack of care to their duties or other people ('gross negligence')
- serious insubordination, for example refusing to take lawful and reasonable orders from a supervisor
What is seen as gross misconduct can depend on the business, so your workplace might have its own policy or rules with examples.